
Auto Circle button
The Circle auto option allows you to define a circle measurement. This measurement type is particularly useful when the circle is positioned in a specific plane that is not parallel with any of the workplanes, or if equally spaced hits are required for partial circles. At least three hits are necessary to measure a circle. The default number of hits needed to measure a circle is based on the default in SETUP mode.
To access the Circle option, access the Auto Feature dialog box for a Circle (Insert | Feature | Auto | Circle).
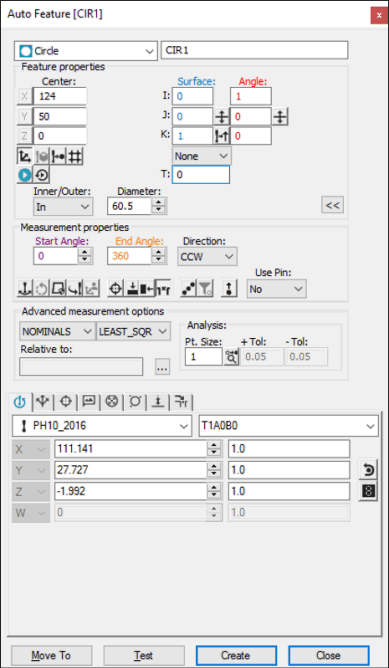
Auto Feature dialog box - Circle
With the dialog box open, use one of these methods to create the feature:
Using Surface Data on the Screen
To generate a circle using surface data:
From the Graphic Modes
toolbar, click the Surface Mode icon ( ).
).
Click once either outside or inside the desired circle. The dialog box displays the center point and diameter from the CAD data of the selected auto circle closest to where you clicked on the part model.
Make any other modifications to the dialog box as needed.
Click Create.
Using Surface Data with the CMM
To generate a circle using surface data with the CMM, take a minimum of three hits in the hole or on the stud. PC-DMIS pierces the CAD surface closest to where the probe touched. The displayed X, Y, Z values reflect the closest CAD circle, not the actual hits. The I, J, K reflects the surface normal vector. If a CAD circle is not found, PC-DMIS displays the closest point and asks that you take the additional hits.
You should select the Find Noms option in the Mode list for this measurement method. For more information on nominals, see the "Mode List" topic in the PC-DMIS Core documentation.
Using Wireframe Data on the Screen
Wireframe CAD data also can be used to generate an auto circle.
To generate the circle:
Click near the desired wire on the circle. PC-DMIS highlights the selected circle closest to where you clicked on the part model.
Verify that the correct feature has been selected. The probe approach is always perpendicular to the feature, as well as perpendicular to the current probe centerline vector. The dialog box displays the value of the selected circle's center point and diameter once the wire has been indicated.
Make any other modifications to the dialog box and the Probe Toolbox as needed.
Click Create.
If the underlying CAD element is not a circle or arc, additional clicks may be necessary to identify the feature. If PC-DMIS doesn't highlight the correct feature, try to click on at least two additional locations of the circle.
Without Using CAD Data
To generate the circle without the use of CAD data:
Take three hits on the surface to find the plane that the circle is lying in.
Take three additional hits in the hole (or on the stud). PC-DMIS calculates the auto circle using all three hits. Additional hits can be taken. PC-DMIS uses the data from all of the measured hits until the Create button is clicked. The X, Y, Z that is displayed is the calculated center of the circle (or stud).
Make any other modifications to the dialog box and the Contact Path Properties tab of the Probe Toolbox as needed.
Click Create.
Typing the Data
This method allows you to type the desired X, Y, Z, I, J, K center value for the circle.
Type the desired X, Y, Z, I, J, K values for the feature into the dialog box.
Click Create to insert the feature into your measurement routine.
Gage Scan Calibration
The Circle auto option offers the Gage Scan Calibration strategy to calibrate a probe tip for use with the gage scan filter. For more information, see "Using the Gage Scan Calibration Strategy".