

Auto High Point button
Use the Auto High Point option to search a user-defined search region to locate the highest point in the current workplane. This samples the region itself for the highest point. It does not search existing points in your measurement routine.
View High Point Example:
When you execute a High Point feature, PC-DMIS searches for and then returns
the highest point within the search region. The result of the search is
a single point defined by its X, Y, and Z coordinates and approach vector.
To access the High Point option, open the Auto Feature dialog box for a High Point (Insert | Feature | Auto | Point | High).
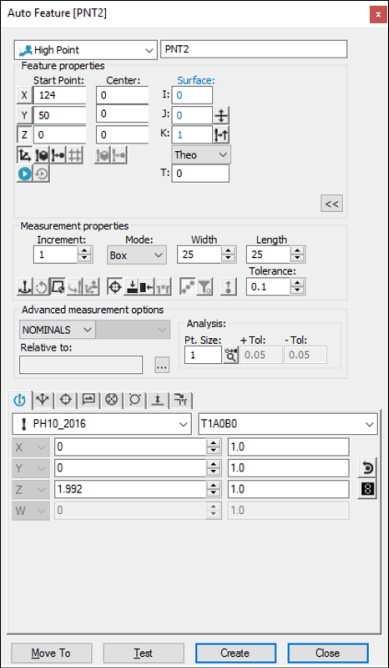
Auto Feature dialog box - High Point
With the Auto Feature dialog box open, use one of the following methods to create the feature:
Using Surface Data on the Screen
To define the High Point search area using surface data, perform the following steps:
Ensure that your alignment's working plane matches the surface vector that you want to use in the High Point calculation.
For example, suppose in your alignment that the back of your part has a Y+ vector. To calculate the High Point on that Y+ surface, you need to change your active work plane to YPLUS.
Select the High Point option in the Auto Feature dialog box.
Position the mouse pointer in the Graphic Display window to indicate the desired location of the start point (on the surface).
Click once to define the Center of the search region and the Start Point of the search as the same point. PC-DMIS highlights the selected surface.
Click again to define a different Start Point. As long as the dialog box remains open, every odd-numbered click on the part model's surface defines the Center and the Start Point to be the same as the clicked location. Every even-numbered click defines a new Start Point location only.
Verify that the correct surface has been selected.
PC-DMIS pierces the highlighted surface and displays the location
and vector of the selected point. The direction of the surface normal
vector is determined by the side of the part that is accessible to
the probe. If both sides of the part are equally accessible, the normal
from the CAD data is used. The Flip Vector
icon ( ) on the dialog box lets you change the probe's
approach direction.
) on the dialog box lets you change the probe's
approach direction.
Define the type of search zone. To do this, in the Measurement Properties area, in the Mode list, choose either Circular or Box.
Define the size of the search zone:
For a box type search zone, change the values in the Width and Length boxes.
For the circular type search zone, change the values in the Inner Radius and Outer Radius boxes.
PC-DMIS displays the search zone in the highlight color.
Define the Increment and Tolerance values for the High Point procedure to use.
Make any other changes that you need in the dialog box.
Click Create to insert the feature into the measurement routine.
Using Surface Data with the CMM
To define the search region for the High Point with the CMM, perform the following steps:
Ensure that your alignment's working plane matches the surface vector that you want to use in the High Point calculation.
Select the High Point option in the Auto Feature dialog box.
With the probe, touch once on the desired surface of the part. This defines the Center of the search region and the Start Point of the search as the same point. PC-DMIS highlights the selected surface.
If you want a different search center, at the desired surface location, touch the probe again. This defines a new center for the search region. If you sample another location with the probe, it changes the location of the start point and approach vector. Each consecutive sample that you take alternates between the search center and the start point. Each time that the probe samples the surface of the part, PC-DMIS pierces the CAD surface closest to where the probe touched.
Define the type of search zone. To do this, in the Measurement Properties area, in the Mode list, choose either Circular or Box.
Define the size of the search zone:
For a box type search zone, change the values in the Width and Length boxes for a box type search zone.
For the circular type search zone, change the values in the Inner Radius and Outer Radius boxes.
PC-DMIS displays the search zone in the highlight color.
Define the Increment and Tolerance values for the High Point procedure to use.
Make any other changes that you need in the dialog box.
Click Create to insert the feature into the measurement routine.
For this method, make sure that you choose the Find Noms option in the Mode list. For more information on nominals, see the "Mode List" topic in the PC-DMIS Core documentation.
Without Using CAD Data
You can generate a High Point without the use of CAD data.
Ensure that your alignment's working plane matches the surface vector that you want to use in the High Point calculation.
Select the High Point option in the Auto Feature dialog box.
With the probe, touch the part's surface once.
The location you probe indicates the X, Y, and Z nominal for both the search's Start Point and the search zone's Center.
PC-DMIS also displays the I, J, K approach vector of that hit. This vector points away from the surface.
To define a different start point, touch the part's surface again where you want the start point. More touches on the part alternate between the start point and the search center.
Define the type of search zone. To do this, in the Measurement Properties area, in the Mode list, choose either Circular or Box.
Define the size of the search zone:
For a box type search zone, change the values in the Width and Length boxes for a box type search zone.
For the circular type search zone, change the values in the Inner Radius and Outer Radius boxes.
PC-DMIS displays the search zone in the highlight color.
Define the Increment and Tolerance values for the High Point procedure to use.
Make any other changes that you need in the dialog box.
Click Create to insert the feature into the measurement routine.
Typing the Data
With this method, you can type the exact center of the search region. You can also type the approach vector.
Ensure that your alignment's working plane matches the surface vector that you want to use in the High Point calculation.
Select the High Point option in the Auto Feature dialog box.
Under Center, type the X, Y, and Z values to define center of the search region.
Under Start Point, type the X, Y, and Z values to define start location of the search.
Under Surface, type the I, J, and K values to define the approach vector.
Define the type of search zone. To do this, in the Measurement Properties area, in the Mode list, choose either Circular or Box.
Define the size of the search zone:
For a box type search zone, change the values in the Width and Length boxes for a box type search zone.
For the circular type search zone, change the values in the Inner Radius and Outer Radius boxes.
PC-DMIS displays the search zone in the highlight color.