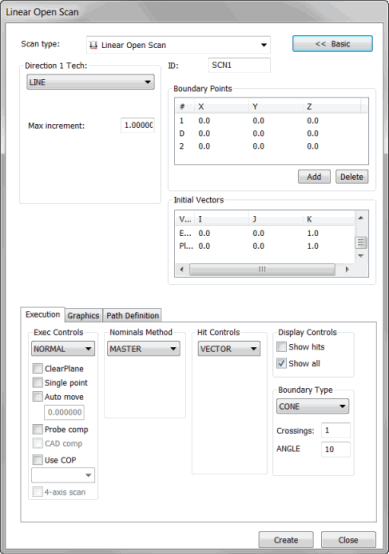

Linear Open Scan dialog box
The Insert | Scan | Linear Open method scans the surface along an open-ended line. This procedure uses the starting and ending point for the line. It also includes a direction point for the calculation of the cut plane. The probe always remains within the cut plane while it performs the scan.
There are three different types of LINEAROPEN direction techniques, as explained in the "Direction Techniques" area.
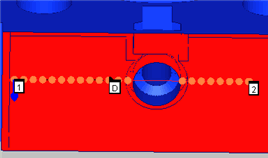
A Sample Linear Open Scan
To Create a Linear Open Scan
Ensure that you have enabled a TTP or an analog probe.
Place PC-DMIS into DCC mode.
Select Insert | Scan | Linear Open to open the Linear Open Scan dialog box.
If you want to use a custom name, type the name of the scan in the ID box.
Select the appropriate LINEAROPEN type from the Direction 1 Tech list.
Depending on your type of LINEAROPEN scan, type the appropriate increment and angle values into the Max Incr, Min Incr, Max Angle, and Min Angle boxes.
If you want your scan to traverse some of the surfaces between the start and end points but not all the surfaces, use the Select check box and select those surfaces. For information, see "Graphics Tab".
Add the 1 point (starting point), the D point (direction to scan), and the 2 point (ending point) to the scan by following an appropriate procedure as discussed in "Boundary Points area".
If you want to scan all the surfaces between the start and end points, you no longer need to select all those surfaces. You can have PC-DMIS automatically scan across all those surfaces like this:
After you've selected the 1, D, and 2 points, access the Advanced section of the Graphics tab.
Mark the Select check box. Then click Deselect All to deselect any selected surfaces. When you select the Generate button later in this procedure, PC-DMIS automatically generates the scan across all surfaces between the start and end points.
Select the appropriate type of hits to take from the Hit Type list in the Hit Controls area.
Make any needed changes to the vectors in the Initial Vectors area. To do this, double-click on the vector, make any changes in the Edit Scan Item dialog box, and then click OK to return to the Linear Open Scan dialog box.
Select the appropriate nominals mode from the Nominals list in the Nominals Method area.
In the Tolerance box in the Nominals Method area, type a tolerance value that at least compensates for the probe's radius.
Select the appropriate execution mode from the Execute list in the Exec Control area.
If you are using a thin part, type the part's thickness in the Thickness box in the Graphics tab.
If needed, select any of the check boxes from the areas on the Execution tab.
If you are using an analog probe, consider using the Control Points tab to optimally run your scan.
Click the Generate button in the Theoretical Path area on the Path Definition tab to generate a preview of the scan on the CAD model in the Graphic Display window. When you generate the scan, PC-DMIS starts the scan at the start point and follows the chosen direction until it reaches the end point.
If you want to delete individual points, select them one at a time from the Theoretical Path area, and press the Delete key.
If desired, use the Spline Path area on the same tab to fit the theoretical path to a spline path.
Make additional modifications to your scan as needed.
Click the Create button. PC-DMIS inserts the scan into the Edit window.
To Use the Quick Scan Feature to Create a Linear Open Scan
You can use Quick Scan functionality to create a Linear Open scan in Curve mode or Surface mode from a polyline or surface. For details, see "Creating Quick Scans".
To Create a Linear Open Scan in Curve Mode
If your CAD has curves or polylines, you can create a Linear Open scan in Curve mode by selecting the Curve Mode icon on the Graphic Modes toolbar (View | Toolbars | Graphic Modes).
When you click to define point 1 on a curve, the curve gets selected. To select multiple curves, press Ctrl and then click on each curve or polyline. The selected curve or polyline will be deselected if you press Ctrl and then click on that curve or polyline again.
The order of selection is important. The scan is generated on the curves or polylines in the order that they are selected. PC-DMIS locates the nearest end of the next polyline from the end point of the scan on the first polyline. This end becomes the starting end of the scan on the next polyline.
Pick 1, D, and 2 points, or just 1 and D points, on the selected curve or polyline. PC-DMIS generates the scan.
There must be a surface behind the polyline or curve to generate the scan.
You can use the edge distance to specify the distance that you want skip from the end of the polyline.
If you select the Jump Hole check box on the Path Definition tab, the probe will lift between the scan on each polyline.
If you clear the Jump Hole check box, the PC-DMIS will scan in a straight line between the end point of the first polyline to the start point of the next polyline.
The scan start point of the first polyline is the point where you click and create a gesture. If this point is closer than the edge distance that is specified in the scan dialog box, the scan starts from the edge distance away from the end point.
To define the scan on another curve, select the Deselect All button on the Graphics tab in the Linear Open Scan dialog box (Insert | Scan | Linear Open).
To Create a Linear Open Scan on a 3D Wireframe CAD Model
To perform a Linear Open scan on a wireframe model, you should generally use a 3D wireframe CAD file. You need the 3D wires to define the shape of the feature you want to scan, as well as its "depth" (3D aspect). This type of scan follows the same procedure as above.
To Create a Linear Open Scan on a 2D Wireframe CAD Model
If you absolutely must perform a Linear Open scan on a 2D wireframe file, you can do so with some extra work.
Import the 2D CAD file. The CAD origin needs to be on the CAD some place and not off in body coordinates (this makes things easier).
Select Insert | Feature | Construct | Line. The Construct Line dialog box appears.
Choose Alignment. This constructs a line at the CAD origin and normal to the surface of the 2D CAD data.
Open the Edit window. If you are using millimeters for your units of measurement, change the length of the line from 1 (the default) to something longer, such as 5 or 10. For measurement routines that use inches, ignore this step.
Export the measurement routine (the features only) to either an IGES or DXF file type. Store the exported file to a directory of your choice.
Return to your measurement routine. Delete the alignment line that you created.
Import the file that you just exported back into the same measurement routine. When PC-DMIS prompts, click Merge to merge the CAD wire into your Graphic Display window. Your CAD model should now have a CAD wire normal to the rest of the other CAD wires.
Open the Linear Open Scan dialog box.
Click on the Graphics tab and then select the Select check box.
Click each wire that defines the feature to be scanned. Select them in the order that they will be scanned, starting with the wire where the scan will start.
Select the Depth check box.
Click on the imported wire that is normal to all the other wires.
Clear the Select check box. You can now select your 1, D, and 2 boundary points on the theoretical surface defined by the wires that define the surface's shape and the wire defining the depth.
If PC-DMIS is in Online mode, select the Measure check box. Select FindNoms from the Nominals Method area. In the Tolerance box, select a good tolerance value.
Click Create. PC-DMIS inserts the scan. If it is in Online mode, it begins the scan and finds the nominals.