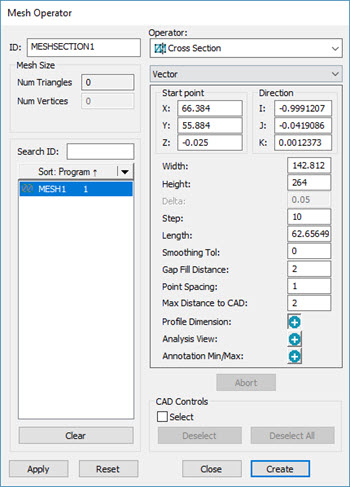

Mesh Operator dialog box - CROSS SECTION operator
The Mesh CROSS SECTION operation generates a subset of polylines determined by the defined intersection of a set of parallel planes with the Mesh object. The software defines the set of planes by the start point, direction vector, step distance between the planes, and length. The software determines the number of planes by the Step distance divided into the Length plus one.
You can evaluate the Mesh CROSS SECTION operator by the profile dimension.
To apply the CROSS SECTION operation to a Mesh:
From the Mesh toolbar
(View | Toolbars | Mesh), click the Cross Section a Mesh button ( )
to open the Mesh Operator dialog box. You
can also click the Insert | Mesh | Operator
menu option.
)
to open the Mesh Operator dialog box. You
can also click the Insert | Mesh | Operator
menu option.
From the Mesh Operator dialog box, select Cross Section from the Operator list.
From the Mesh toolbar, click
the 2D Section Slide Show button  to display cross sections in 2D view. For details,
see the "Cross
Section Slide Show" section of the "Show
and Hide Cross Section Polylines" topic.
to display cross sections in 2D view. For details,
see the "Cross
Section Slide Show" section of the "Show
and Hide Cross Section Polylines" topic.
The list underneath the Operator list contains these options: Vector, Axis, Curve, and 2 Points. For details on how the Curve function works, see the "Creating a Cross Section along a Curve" topic. For details on the 2 Points option, see the "Creating a Cross Section between 2 Points" topic.
The Mesh CROSS SECTION operator uses the following options:
Start point: This option indicates the coordinates of a point belonging to the first plane cutting the mesh. The software displays the start point as a blue ball in the Graphic Display window. You can use the ball as a handle to drag to a new location. The software defines the start point by the first click in the Graphic Display window. In the actual Edit window command, the start point value is held in the START PT parameter.
Direction (applies only to the Vector and 2 Points options): This value indicates the direction of the normal vector. You can define it by the first click in the Graphic Display window. In the actual Edit window command, the software holds the Direction value in the NORMAL parameter.
Axis (applies only to the Axis option): Use this option to create a cross section along the X, Y, or Z axis. Select the desired axis (the default is X), set a start point in the Graphic Display window, and set an end point. The section plane cuts the part at a given step value over the length of the cross section.
Width: This value indicates the width of the section under consideration. If the value is 0, the system calculates the value as the CAD bounding box value.
Height: This value indicates the height of the section under consideration. If the value is 0, the system calculates the value as the CAD bounding box value.
Delta: The software does not use this value for Mesh cross sections.
Step: This value indicates the distance between the planes. In the actual Edit window command, the software holds the step value in the INCREMENT parameter.
If the Step value is greater than the Length value, the software creates only one section cut at the start point.
Length: This value indicates the maximum distance between the first and last plane. The software displays the length value in the Length parameter of the dialog box. PC-DMIS displays it as a purple line in the Graphic Display window.
Smoothing Tol: Set to 0 (zero) to turn off smoothing (the default value).
Use Smoothing Tol to remove small steps in the cross section and create a smoother measured polyline. This setting filters out the points within the smoothing tolerance value and then fits a polyline to the data using the Point Spacing value.
You can also define Point Spacing with the CrossSectionCopCadCrossSectionStep registry entry. For details on this registry entry, see "CrossSectionCopCadCrossSectionStep" in the PC-DMIS Settings Editor documentation.
You should set the Smoothing Tol very small so that the measured cross section does not deviate greatly from the actual data. Except for extreme situations (for example, a very large CAD model and/or a very poor density of points), you should set this parameter between a few tenths of a mm (maximum) and a few thousandths of a mm (minimum).
Gap Fill Distance: This value defines the maximum gap distance along the yellow measured polylines of a cross section. If gaps equal to or smaller than this value appear, the gaps are filled in with calculated points. You can also set this value in the PC-DMIS Settings Editor. For details, see the "CrossSectionMaximumEmptyLength" topic in the PC-DMIS Settings Editor documentation.
Point Spacing: Use this entry only when the CrossSectionCopCadCrossSectionDrivenByCad registry entry is set to 1 (True). This value is the step used along the CAD polylines to look for the best interpolated Mesh point. For greater accuracy, or if the CAD model is very small, you can set this value to a smaller value. You can also set this value in the PC-DMIS Settings Editor. For details, see the "CrossSectionCopCadCrossSectionStep" topic in the PC-DMIS Settings Editor documentation.
Max Distance to CAD: The value defines the maximum distance of the Mesh data relative to the nominal CAD model. The default value is 2 mm. If the Mesh data object deviates more than the Max Distance to CAD value from the CAD model, the software may not compute the yellow measured cross section. You can adjust this value to account for large deviations of the Mesh data relative to the CAD model.
Profile Dimension:
Click the Add button  to create a new profile dimension for each cross section. For details
on Profile Dimension, see "Dimensioning
Profile - Line or Surface" in the "Using
Legacy Dimensions" chapter of the PC-DMIS Core documentation.
to create a new profile dimension for each cross section. For details
on Profile Dimension, see "Dimensioning
Profile - Line or Surface" in the "Using
Legacy Dimensions" chapter of the PC-DMIS Core documentation.
Analysis View: Click the Add button to create the ANALYSISVIEW command in the Edit window. For details on the ANALYSISVIEW command, see "Create Analysis View Command" in the "Inserting Report Commands" chapter in the PC-DMIS Core documentation.
Annotation Min/Max: Click the Add button to create the minimum and maximum values in the form of annotation labels for the active cross section.

PC-DMIS calculates the minimum and maximum points each time you execute the measurement routine.
CAD Controls: Mark the Select check box to select CAD surfaces in the Graphic Display window. PC-DMIS filters out any cross sections that do not pass through the selected surfaces when you click Create.
For example, if you select surface A after you define the start and end points, the software only creates the cross sections at B and C:
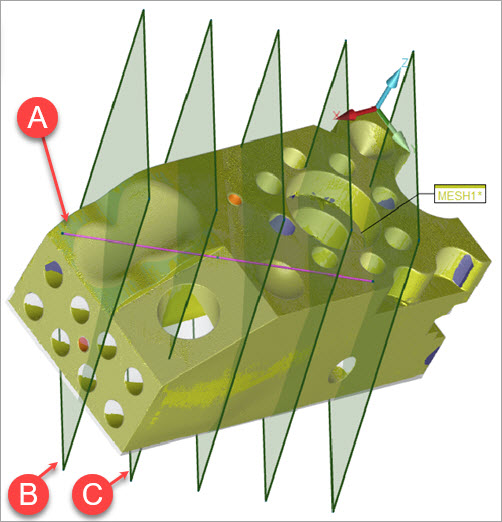
Example of a selected surface (A) limiting the cross sections to only (B) and (C)
Selected surfaces do not affect what you see when you click the View button.
When the cutting planes are visible in the Graphic Display window, it is possible to manipulate them as follows:
Select a plane’s edge handle and drag to resize the height and width of the cutting planes.
Select a plane’s corner handle and drag to rotate the set of planes around their axis.
Select the first or last purple length line’s blue point handle, and then drag to redefine the purple line's START or END definition. With the change in direction, the software updates the values in the dialog box and the number of planes in the Graphic Display window. In the case of Axis mode, the direction of the planes does not change.
Select and drag the purple length line’s middle blue point handle to move the set of planes.
When you create or edit a cross section, the cutting planes appear in a transparent view as shown above.
Click Create to:
Insert a MESH/OPER,CROSS SECTION command for each plane into the Edit window.
For example:
MESHSECTION3=MESH/OPER,Cross Section,TOLERANCE=0.05,WIDTH=117.715,HEIGHT=227.086,
START PT = -6.439,60.097,6.276,NORMAL = 0.9684394,-0.2221293,-0.1130655,SIZE=76
REF,MESH1,,
The black polylines represent the nominal CAD, the yellow polylines represent the measured polyline.
Insert a label for each plane into the Graphic Display window as shown below:
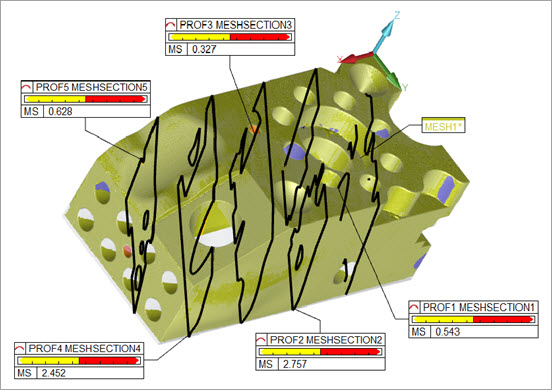
Finished cross sections showing five planes
Defining the Cross Section by Typing Values
Use the Mesh Operator dialog box to enter any of these values:
START PT: This value specifies the cross section's starting point using the Start Point X, Y and Z boxes.
NORMAL: This value specifies the cross section's vector using the Direction I, J and K boxes.
WIDTH: This specifies the value of the cross section's width property in the Width box.
HEIGHT: This specifies the value of the cross section's height property in the Height box.
TOLERANCE: This specifies the value PC-DMIS uses to determine the maximum distance from the plane a point must be in order for PC-DMIS to consider it as part of the cross section in the Delta box.
INCREMENT: This specifies the value between cutting planes in the Step box.
LENGTH: This specifies the value between the first and last cutting planes in the Length box.
SMOOTHING TOLERANCE: This specifies the tolerance value to refine the points associated with the generated cross section in the Smoothing Tol box.
Defining the Cross Section by Using the Graphic Display Window
To define some of the cross section parameters, click the CAD model in the Graphic Display window to select the Start Point. A pink line appears. Click a second point on the CAD model to determine the Direction vector and the Length.
Creating a Profile Dimension from the Graphic Display Window
When you double-click a cross section label, PC-DMIS creates a new profile dimension that evaluates the selected cross section.
Exporting Mesh Cross Sections in IGES Format
Once you create the Mesh cross sections, you can export them in IGES format from the Mesh Operator dialog box.
For details on the Mesh Export operator, see "Mesh EXPORT Operator" in this documentation.
More:
Creating a Cross Section along a Curve
Creating a Cross Section between 2 Points
Show and Hide Cross Section Polylines