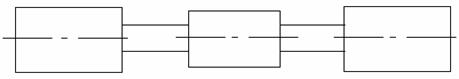
Runout dimensioning is generally used in camshaft operations. A camshaft is designed to rotate around a center line. Since the separate cylinders comprising the camshaft are all on the same center line, you need to ensure that the centerline is not only parallel, but that the cylinders are also coaxial (or concentric).

Sample Camshaft
Additionally, you need to make sure the surface of the cylinders is round and straight (straight when compared to a separate datum axis, not just its own axis).
The main difference between runout and parallelism is that runout is checking points on a surface of a cylinder, and not just the axis of the cylinder. Runout also differs from a cylinder's straightness because it compares the surface of the cylinder to a datum axis, not just to itself. A runout dimension checks for these conditions.
More: