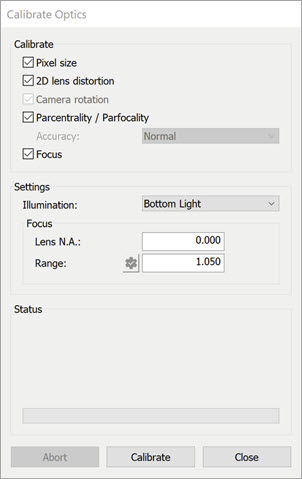
Calibrate Optics dialog box
This option calibrates the optics on the system. PC-DMIS supports five separate calibrations (depending on hardware and the available calibration artifact):
Pixel Size - This calibration method calibrates the size of the field of view (FOV) throughout the zoom cell's magnification (mag) range or with a given optic’s configuration. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines on optical calibration intervals. You need to recalibrate the optical magnification any time the zoom cell or microscope is altered (such as when it is sent in for repair).
2D lens distortion - This calibration method calibrates the non-linear errors in the FOV throughout the zoom cell's magnification range or for a given optics configuration. This can significantly improve measurement accuracy away from the center of the FOV, especially on lower magnification optics.
Camera Rotation - This calibration method calibrates the rotation of the camera to the stage and removes any rotation. This is particularly evident on CMM-V systems.
Parcentrality/Parfocality - This calibration method ensures that the center of the lens and the center of the FOV are aligned. This option is only available if the following are true:
You are using a zoom lens.
The selected lamp was previously calibrated. See "Calibrate Illumination".
You selected the Pixel Size calibration.
Focus - This is the Focus Depth and Latency calibration method which are calibrated through a series of focus adjustments at various magnification levels.
If your zoom cell automatically calibrates, then you won't need to perform a specific magnification calibration. Instead, PC-DMIS displays a message when it completes the calibration process.
To calibrate the optics, follow these steps:
From the list on the Calibrate Probe dialog box, select Calibrate Optics.
Click Calibrate to open the Calibrate Optics dialog box.

Calibrate Optics dialog box
When the calibration procedure starts, DO NOT move the calibration standard.
From the Calibrate area, select the needed options.
Pixel Size - This option calibrates the pixel size at a different magnification to determine the size of a measured feature.
2D lens distortion - This option calibrates for any 2D distortion in the camera image.
Camera Rotation - This option allows PC-DMIS Vision to determine if there is any rotation in the camera relative to the stage. PC-DMIS then makes the necessary adjustments. The software automatically enables this option if you enable the 2D lens distortion calibration option.
Parcentrality/Parfocality - When you select this option, PC-DMIS performs the parcentrality/parfocality calibration using the Pixel size calibration. This process replaces the need to do an Optical Center calibration. This option is only available when you use the HexagonMI Slide (Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence) and when your machine uses a zoom lens. Use the "Calibrate Optical Center" option for machines using a fixed (non-zoom) lens. Also, see the "Parcentricity Calibration Modes" topic.
Accuracy - There are two methods for calibrating parcentrality/parfocality:
Normal - This method does the calibration on the same rectangles that were used for the FOV (pixel size) calibration. This method results in a faster calibration process.
High - This method does the calibration on the concentric circles on the calibration standard. This method gives better quality results, but it takes longer to perform.
Focus - This option performs focus calibration for depth and latency.
From the Settings area, select the calibration settings:
Illumination - Select the Illumination source. Calibration is usually best done with bottom or sub-stage lighting as the edge contrast is sharper. Select <Current> to use the current illumination settings and not change the illumination during calibration. CMM-V can now use its ring light, and CMM-V defaults to that light source.
Focus - Lens N.A. - Specify the numeric aperture (N.A.) of the current lens if known; otherwise, leave this box blank. This value allows the calibration program to optimize the focus used during the calibration.
Focus - Range - Specify the focus range if no numeric aperture is given. This provides the range over which the focus is done.
Auto Range - Select this check box to auto calculate the best focus range to use. (This option may not be available on all systems.)
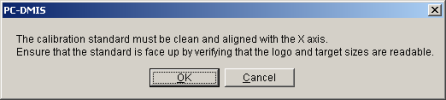
Click the Calibrate button. The software displays a message box stating that your calibration standard must be clean and aligned with the X axis. You must also ensure that the standard is face up.
Although the calibration processing employs noise and dirt rejection techniques, a dirty calibration standard may trigger calibration failures or yield less accurate measurement values. Be sure to clean any dust, dirt, fingerprints, or other material from the calibration standard's glass portion. Use a mild non-depositing cleaning solution, such as rubbing alcohol, and a soft, lint-free cloth. Be sure to also clean the stage glass where the calibration standard is positioned. For proper cleaning techniques, refer to your hardware documentation. If the stage carrying the glass standard might move during the calibration sequence, hold the standard to the stage with clay or putty.
Place the calibration artifact on the stage so the length of the standard runs along the X axis of the machine. For the ROI slides, ensure that the larger targets are on the left (-X direction) and the smaller targets on the right (+X direction). Verify the alignment with the X axis by watching the horizontal line on the standard while traversing the stage X axis. The line should remain in the field of view and ideally very near center.
Click the OK button. Additional messages appear, requesting that you center the target.
Place a target so that it completely fits within the camera's view. This target should be roughly centered within the FOV and focused. The focus does not need to be optimal, just a good starting place for the software focus process.
Click the OK button. If you have a DCC machine, it automatically focuses on the target. If you have a manual machine, the software displays a prompt for you to focus on the target.
Use the manual controls to move the optical measuring system and roughly center the rectangle or square calibration standard in the FOV. PC-DMIS determines the target size based on your optics.
Do not change the Z position or the focus during the rest of the calibration procedure.
Click OK after you have centered the target. The calibration routine automatically proceeds based on the calibration options you selected:
If the machine supports DCC illumination control, and an illumination lamp has been selected in the Illumination field, PC-DMIS Vision performs a lighting grayscale adjustment where it measures the target (or series of targets) across the range of magnifications.
If the system has Manual Illumination control, you are prompted to increase or decrease the illumination level as required.
If you select Pixel Size, PC-DMIS measures the series of calibration targets automatically.
![]()
Pixel Size Calibration
If you select 2D lens distortion, at each magnification in the Pixel Size calibration, PC-DMIS Vision measures one or more solid circle targets in a rectangular pattern that covers most of the FOV. If the software doesn't automatically locate the first circle, PC-DMIS Vision prompts you to move the specified circle to the center of the FOV.

2D lens distortion
If under Parcentrality / Parfocality, under the Accuracy drop-down list, you chose Normal, PC-DMIS Vision performs Parcentrality/Parfocality calibration on the same rectangles that it used for the Pixel Size calibration.
If you chose Focus, the system moves in and out of focus at various levels of magnification. PC-DMIS does focus calibrations to determine focus depth and focus latency.

Focus Calibration
If you chose Camera Rotation, PC-DMIS Vision measures the line at the bottom of the slide at different positions multiple times to identify the camera-to-stage rotation. If the rotation angle that PC-DMIS calculates is greater than five degrees, a warning indicates that the hardware should be physically adjusted to make the angle smaller. You can still apply the calibration to compensate, but it is recommended that you get the physical wrist/camera adjusted to the stage.

Camera Rotation Calibration
If under Parcentrality / Parfocality, under the Accuracy drop-down list, you chose High, PC-DMIS Vision prompts you to "Align the HexagonMI Standard Concentric Circle in Target". Align the circle as depicted in the image below, and click OK.
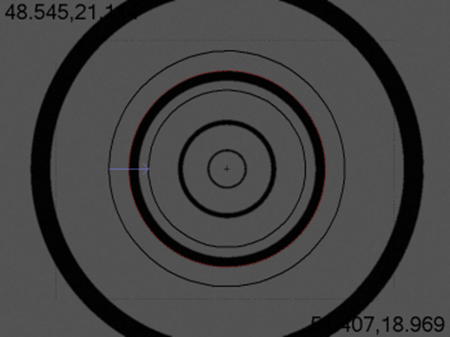
Target centered on Concentric Circles of HexagonMI Standard
The Calibration Process continues. It focuses and takes a series of measurements at different magnification levels. This process establishes that the optical center and focal depth coincide through the focal range. This means if you focus and measure a circle at one magnification, it gives the same XYZ position at another magnification.
Near the end of calibration, PC-DMIS generates and runs a series of dynamic measurement routines in the background. It does this to perform a basic verification that measures a subset of the calibration data. As the software measures each target in these measurement routines, the Status area on the Calibrate Optics dialog box updates its message to show the step number.
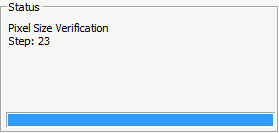
Status Message Showing Pixel Size and Error
There is a pixel size verification which is turned off by default and is controlled by the ProbeQualVisionOpticsCalPixelSizeVerifyEnabled registry entry in the PC-DMIS Settings Editor. If this registry is enabled, then at the end of calibration, PC-DMIS performs a basic verification that measures a subset of the calibration data. As the software measures each target in these measurement routines, the Status area on the Calibrate Optics dialog box updates its message to show the step number.
![]()
Verification Complete dialog box
If the Pixel Size Verification dialog box appears, you can click Run Again to re-run the verification. This helps determine if any errors were simply anomalies in the verification. If the verification fails multiple times, try and re-run the entire pixel size calibration. If both the calibration and the verification fail repeatedly, contact Hexagon Technical Support.
Click Continue to accept the results of the verification.
The ProbeCal section of the PC-DMIS Settings Editor contains registry entries that affect the pixel size calibration.
Click the Close button to close the Calibrate Optics dialog box. The software also writes the calibration results to the Calibration Results dialog box so that you can view the results of the calibration later. To view the results, click the Results button on the Probe Utilities dialog box:
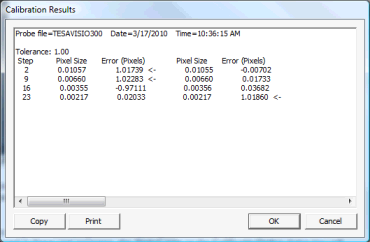
Calibration Results dialog box
You have now calibrated the field of view. Repeat this process for each lens you wish to use on the machine.
On a CMM-V camera, you only need to calibrate the FOV for the A0B0 wrist angle. You may wish to place some reflective white paper on the CMM table under the "Calibration Artifact Holder" (Part Num. CALB-0001). The "Calibration Artifact Holder" includes a glass slide (CALB-0002) and a ring gage (CALB-0003). The artifact holder is used for calibration of the CMM-V camera.