Stacked Rotary Table
Stacked rotary tables provide the ability of rotating a part or calibration artifact beyond the standard XYZ axes.
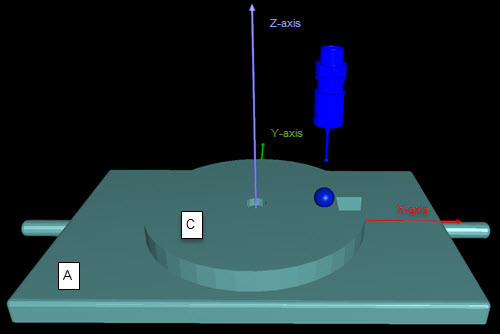
A stacked table system has two tables stacked on top of each other. The bottom table is typically labeled "A" and the top table is typically labeled "C".

A - Table A, bottom table
C - Table C, top table
Details of a stacked rotary table
In this scenario, the "C" table rotates about the Z axis and the "A" table rotates about the X axis.
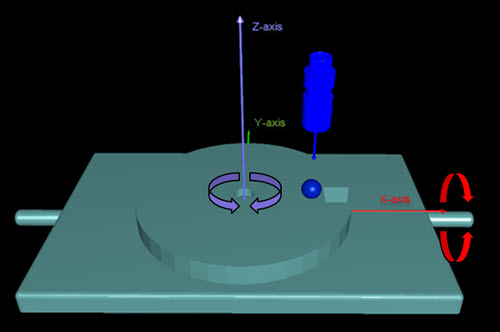
Table rotation directions
The following four images show a real-world example of the A table on a stacked rotary table as it rotates 90 degrees.
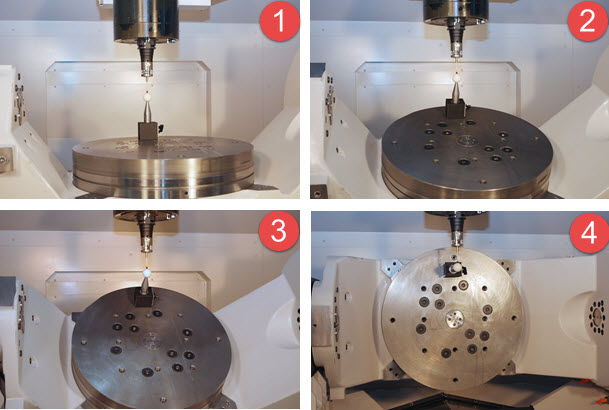
Example of a stacked rotary table as it rotates 90 degrees
Dual Rotary Table
The configuration of a Dual Rotary Table system has these properties:
It is comprised of two independent rotary tables as typically seen on multitasking machines.
Each table represents a lathe spindle. You define one spindle as the main spindle, and the other as the secondary spindle.
The tables within the machine must be far enough apart from each other to provide the necessary operating space.
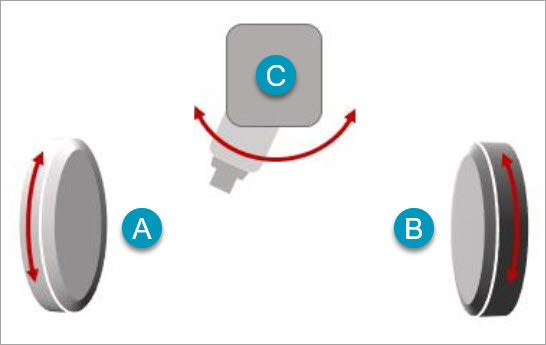
Example of a typical multitasking machine setup with two independent rotary tables (A and B) and a single axis rotary head (C)
On a multitasking machine, both rotary tables (A and B) are lathe spindles and are powered separately. The single axis rotary head (C) is a positional milling spindle. The spindles turn at very high speeds and are used to cut (or mill) stationary parts. With two lathe spindles and a positional milling spindle, this is what makes a multitasking machine special. You can use it to completely manufacture all sides of a part, which allows you to have two parts in various stages of completion on the machine. You can cut on both lathe spindles independently and at the same time. In most cases you can also transfer a part clamped in one lathe spindle to the other automatically. For example, you can drive the B table to the A table until the jaws on the B table can grab the part from the A table.
If you want to control two independent rotary tables, you should use two separate measurement routines, one for each table.
On non-multitasking machines, you can only have one table active at a time. You can select the active table from the Active Rotary Table toolbar. Once you activate a table, it remains active for the entire length of the measurement program. The other table stays inactive.
You can calibrate and use the active table just as you would a single table system.
More: