
Spline Path area
The Spline Path area on the Path Definition tab in the scan dialog box (Insert | Scan) contains several options that you can use to create a spline path to which your scan's theoretical path will be fitted.
This option is not available for Perimeter, Rotary, UV, and Grid scans.
To create a theoretical path and fit it to a spline path, do the following:
Select a scan type that supports a spline path (Linear Open, Linear Closed, Patch, Section, or Freeform).
Select the Path Definition tab.
Define the theoretical path. In the case of the Freeform scan, you can use the Read File button to import a pre-existing set of theoretical data points, or click Generate. The Generate button automatically generates a set of theoretical data points between your starting point and ending point from the existing CAD data.
In the case of the Freeform scan, the Generate button does not exist. Instead, click on the CAD itself to select the theoretical points.
The points appear in the Theoretical Path list and show their XYZ and IJK data. As long as you have more than five points in the Theoretical Path list, you can fit it to a spline path by using the Calculate button in the Spline Path area. You don't have to fit the theoretical path to a spline path, but if the theoretical path list contains too many points, then you want to use the spline function to reduce or spread the points equally.
Define the parameters as described below for the spline path to which you will fit the theoretical path.
When the Theoretical Path and Spline Path areas are filled out, click Calculate in the Spline Path area. PC-DMIS changes the theoretical data to fit the parameters that you specified in the Spline Path area.
When you have the points as you like them, click Create to generate the scan.
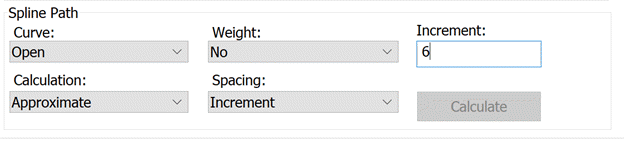
The Spline Path area offers the following choices:
Curve
list
This list contains two options: Open and Closed. An open curve passes through the start,
control, and end points and then stops. A closed curve does the same,
but when the curve passes through the end point, it also returns to the
start point.
Calculation
list
This list contains two options: Approximate and
Interpolated. It determines whether the spline
path passes through points in the spline (interpolated) or simply approaches
the points (approximate). Interpolated results
in sharper curves. Approximate results in smoother
curves.
Weight
list
This list contains two options: Yes and No. What you select determines whether or not
PC-DMIS should give the points a weight when it constructs the spline
path. If you select Yes, PC-DMIS gives them
a weight according to how close they are to other points on the curve.
The further they are from other points, the greater weight they have in
the fitting process.
Spacing
list
This list contains two options: Increment and
Number of Hits.
If you select Increment, PC-DMIS creates the spline path points at a given increment defined by the value in the Increment box.
If you select Number of Hits, PC-DMIS creates the spline path points using and spacing the number of hits you specify in the Number of Hits box.
Increment
or Number of Hits box
This box controls the number of hits along the scan's path.
If you selected Increment in the Spacing list, this box holds the increment value. The distance between two path points is equal to this increment. The smaller the increment, the greater the number of path points.
If you selected Number of Hits in the Spacing list, this box holds the number of hits to space along the theoretical pathway.
For example, if you typed 50, PC-DMIS would attempt to generate fifty points along the scan path.
Calculate
button
This button calculates the spline and fits the theoretical data points
to the spline, usually filtering out several hits. This button only becomes
enabled if you have at least five hits in the Theoretical
Path list.