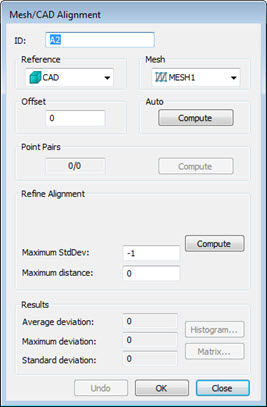

Default view of Mesh/CAD Alignment dialog box
The Mesh/CAD Alignment dialog box contains these options:
ID - This option displays the identification label for the alignment.
Reference - Select the reference object for your alignment, usually either the CAD itself or a defined Mesh. The mesh is aligned to the selected reference.
Mesh - This list lets you choose the mesh to use in the alignment.
Offset - This option defines an offset value for a surface CAD model and is typically used with sheet metal parts. Applying an offset value essentially gives the surface CAD model a thickness so that you can align the mesh data to a different face that isn't represented in the surface CAD model. For example, if you have a surface CAD model for the top of a part, but you want to align to a corresponding bottom surface, you could apply an offset value of the part's thickness to align the scanned data to the bottom side. Use a positive value if you want to apply a thickness in the same direction as the surface normal vector; use a negative value if you want to apply a thickness opposite the surface normal. It is only available for Mesh to CAD alignments.
Auto - This area lets you automatically align the CAD with the mesh with the Compute button. It is only available for Mesh to CAD alignments.
Point Pairs - This area lets you create a rough alignment based on selected points from the CAD that correspond to selected points from the Mesh. Once you have the needed pairs selected, click Compute to perform the rough alignment.
Refine Alignment - This area allows for a more refined alignment. Only the Maximum Distance option is available for Mesh-to-Mesh alignments.
Depending on the alignment being made, the Refine Alignment area of the dialog box may consist of the following items:
Total points - This box defines the number of random sampled points used to refine the alignment. This number must be a value of at least 3. A good number is around 200 points.
Maximum iterations - This box defines the number of repetitions the process makes in order to refine the alignment.
Compute - This button begins the refined alignment process. A progress bar on the status bar shows the progress as the process moves through the alignment iterations.
Maximum StdDev - This box defines the maximum standard deviation used during the execution of an auto alignment. If the entered value is exceeded during the command execution, you are prompted to optionally pick point pairs on the CAD/Pointcloud. A value of -1 disables the Maximum StdDev functionality.
Maximum Distance - This box defines the maximum distance PC-DMIS looks from the CAD for valid Mesh points. If there is no value, PC-DMIS uses the default value of 0 (zero), and the maximum distance becomes half the distance of the CAD bounding box.
Results - This area contains the following items:
Information boxes showing the Average Deviation, Maximum Deviation, and Standard Deviations of the mesh data compared to the CAD model's data.
Histogram - This button takes a random sample of points from the mesh and projects them onto the CAD. The Alignment Histogram dialog box shows the deviations for that sample.
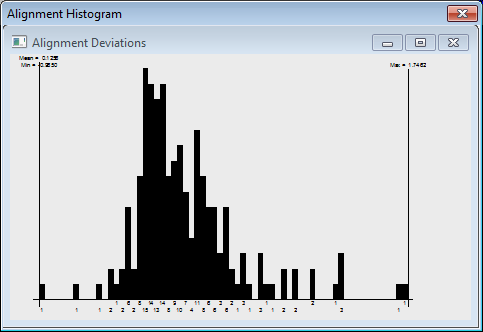
Sample Alignment Histogram dialog box for the selected mesh
Matrix - This button displays the Alignment Matrices dialog box for the mesh alignment. The numerical values of the mesh alignment in offset and rotation matrices are listed.
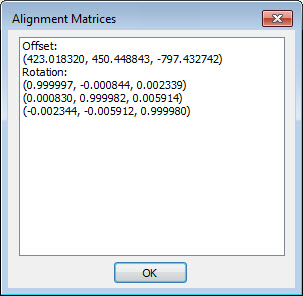
Sample Alignment Matrices dialog box for the alignment