Creating a 2D Radius Gage
To create a 2D Radius Gage with a Cross Section:
Create the cross section.
Select the Cross Section
Slide Show button ( )
from the Pointcloud toolbar (View
| Toolbars | Pointcloud) to view the cross section in a 2D
view.
)
from the Pointcloud toolbar (View
| Toolbars | Pointcloud) to view the cross section in a 2D
view.
Hold the Shift key down and point to the desired
radius. A display widget appears. The display widget shows the nominal,
measured, and deviation values for the radius.
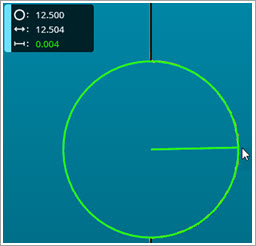
2D Radius Gage display widget
showing the nominal, measured and deviation values for the radius
Click to select the radius. A widget dialog
box appears.
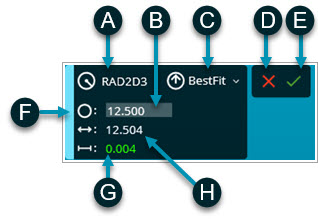
A
- 2D Radius Gage ID
B
- Radius nominal value
C
- Algorithm used to calculate the radius
D
- Cancel button
E
- Create button
F
- Use the handle to move the widget dialog box
G
- Radius deviation value
H
- Radius measured value
2D Radius Gage widget dialog
box
From the widget dialog box,
you can do the following:
Change the 2D Radius
Gage ID (A) and the nominal value (B).
From the list (C), select the algorithm the software uses to
calculate the radius.
Click the Create button (E) to
create the radius gage or the Cancel button
(D) to close the widget dialog box without
creating the radius gage.
Reposition the widget.
To do this, point to the handle on the left side of the widget (F). Click and drag the widget in the Graphic Display
window to reposition it.
When you create the 2D Radius Gage, PC-DMIS
creates its associated command in the Edit window. You can create
additional radius gages as needed.
Once you create a 2D Radius Gage, you can use it in
Location and Distance Dimensions, and Constructions. For Location Dimension,
Form is not supported.
To change the radius settings:
Edit them directly in the Edit window.
Click the radius gage command in the Edit window,
and then press F9 to open the 2D Radius Gage
dialog box to make your changes.
How the 2D Radius Gage is Calculated
Calculating the Nominal
2D Radius
Starting from the initial
picked measured point, the nominal radius is found on the nearest black
polyline. The software calculates the nominal (theoretical) radius for
a least square best fit circle, using all the nominal points that are
within 0.005 mm standard deviation.
Calculating the measured
2D Radius
The software calculates
a least square best fit circle, using the actual points on the yellow
polyline that are associated with the nominal points.
Starting from the initial
picked nominal point, the software finds the radius on the nearest black
polyline. The software calculates the nominal (theoretical) radius for
a least square best fit circle, using all the nominal points that are
within 0.005 mm standard deviation.
Starting from the initial
picked measured point, the software calculates the radius for a least
square best fit circle. The software uses all the measured points within
0.050 mm standard deviation and a search distance of 0.25 mm to find any
additional segments that belong to the radius.
More:
2D
Radius Gage Overview
2D
Radius Gage Dialog Box
 )
from the Pointcloud toolbar (View
| Toolbars | Pointcloud) to view the cross section in a 2D
view.
)
from the Pointcloud toolbar (View
| Toolbars | Pointcloud) to view the cross section in a 2D
view.
