 Calibrating
Perceptron Sensors
Calibrating
Perceptron SensorsThe calibration process described in this step may vary depending on the options you select for laser sensor measurements and the type of installed interface. For detailed information on laser sensor calibration options, see the "Measure Laser Probe Options" topic.

 Calibrating
Perceptron Sensors
Calibrating
Perceptron Sensors
During calibration, PC-DMIS temporarily overrides your current exposure and gray sum values with the default exposure and gray sum values covered in the "Exposure and Gray Sum Settings During Calibration" topic. Once calibration finishes, the software restores your original values.
Use this procedure to calibrate your laser sensor for the first time:
Select Insert | Hardware Definition | Probe to open the Probe Utilities dialog box.
From the Active Tip List box, select the tip that you defined in step 2.
Click Measure to open the Measure Laser Probe dialog box (for information on this dialog box, see "Measure Laser Probe Options").
From Type of Calibration Operation, select one of the options. Then for Perceptron sensors, select Offset.
Define other calibration options as needed: Motion type, Move Speed, Parameter Sets, and Calibration Tool.
If you use a multi-sensor CMM with both a contact probe and a laser probe, make sure a calibrated contact probe first locates the sphere location for the laser calibration tool. This correlates the laser sensor measurement data with the contact probe calibration.
Click Measure to begin the calibration procedure. Follow any on-screen instructions. The first several prompts that you see are identical to the setup procedure for touch-trigger probes.
If you use the MAN or MAN + DCC motion options, or if you answer Yes to the message “Has the sphere moved”, you need to bisect the qualification sphere. For information, see "Bisecting the Calibration Sphere". Once you do an Offset calibration, the software no longer asks you to bisect the sphere unless you answer Yes to the message “Has the sphere moved”.
Certain sensor tip angles may cause the laser beam to fall on a portion of the calibration tool's stem. In some cases, the standard deviation for the sensor calibration of those tips exceeds the expected amount. In those cases, PC-DMIS displays a message to ask if you want to repeat the calibration of those tips. If you click Yes, the system uses the offsets and orientation determined by the first measurement rather than the theoretical values. This results in a clipping around the target that is more accurate during this re-calibration.
Once execution finishes, PC-DMIS returns to Learn mode and opens the Probe Utilities dialog box.
If needed, click Add Angles to define any other tip angles that you need to calibrate.
From the Active Tip List box, select the tips that you want to calibrate. The initial tip calibration only finds offset information for the sensor configuration.
Click Measure to open the Measure Laser Probe dialog box. If you don't select any angles, the software asks if you want to calibrate all the tips.
From the Measure Laser Probe dialog box, select the Tips option.
For Calibration Tool, select the same tool that you used earlier.
Click Measure to begin the tip calibration. Once calibration finishes, PC-DMIS opens the Probe Utilities dialog box.
PC-DMIS stores Offsets of each axis for Perceptron sensors in the registry as HotSpotErrorEstimateX, HotSpotErrorEstimateY, and HotSpotErrorEstimateZ. For details, see "HotSpotErrorEstimateXYZ" in the PC-DMIS Settings Editor documentation.
Once you perform either Offsets or Sensor calibration, depending on the sensor type, you need to perform only steps 8 through 15 on any new probe file that utilizes the same sensor and CMM.

 Calibrating
Portable CMS Laser Sensors
Calibrating
Portable CMS Laser Sensors
Use this procedure to calibrate a portable laser CMS sensor using a planar artifact:
From the Probe Utilities dialog box, click Measure to open the Measure Laser Probe dialog box. For information on this dialog box, see "Measure Laser Probe Options".
Select the appropriate sensor mode. The default is Zoom2A.
Place the planar artifact in a convenient location for the arm to measure.
Click Measure to begin the calibration procedure. Follow any on-screen instructions.
The calibration procedure requires that you take 17 laser stripes on the planar artifact in different positions and orientations with respect to the planar artifact. To help you visualize where to take the stripe, the system draws a yellow target line on the Laser tab in the Graphic Display window.

 Calibrating
DCC CMS Laser Sensors
Calibrating
DCC CMS Laser Sensors
The calibration process described in this step may vary depending on the laser sensor options and the type of installed interface. For detailed information on calibration options, refer to the "Measure Laser Probe Options" topic.
Use this procedure to calibrate your laser sensor for the first time:
Select Insert | Hardware Definition | Probe to open the Probe Utilities dialog box.
From the Active Tip List box, select the tip that you defined in Step 2.
Click Measure to open the Measure Laser Probe dialog box (for information on this dialog box, see "Measure Laser Probe Options").
Select the appropriate sensor mode. The default is Zoom2A.
Define other calibration options as needed: Motion type, Move Speed, Parameter Sets, and Calibration Tool.
If you use a multi-sensor CMM with both a contact probe and a laser probe, make sure a calibrated contact probe first locates the sphere location for the laser calibration tool. This correlates the laser sensor measurement data with the contact probe calibration.
Click Measure to begin the calibration procedure. Follow any on-screen instructions. The first several prompts that you see are identical to the setup procedure for touch-trigger probes.
If you use the MAN or MAN + DCC motion options, or if you answer Yes to the message “Has the sphere moved”, you need to bisect the qualification sphere. For information, see "Bisecting the Calibration Sphere". Once you do an Offset calibration, the software no longer asks you to bisect the sphere unless you answer Yes to the message “Has the sphere moved”.
Once execution finishes, PC-DMIS returns to learn mode and opens the Probe Utilities dialog box.
If needed, click Add Angles to define any other tip angles that you need to calibrate.
From the Active Tip List box, select the tips that you want to calibrate. The initial tip calibration only finds offset information for the sensor configuration.
Click Measure to open the Measure Laser Probe dialog box. If you don't select any angles, the software asks if you want to calibrate all the tips.
From the Measure Laser Probe dialog box, select the appropriate sensor mode. The default is Zoom2A.
Select the Tips option.
For Calibration Tool, select the same tool that you used earlier.
Click Measure to begin the tip calibration. Once calibration finishes, PC-DMIS shows the Probe Utilities dialog box.
Certain sensor tip angles may cause the laser beam to fall on a portion of the calibration tool's stem. In some cases, the standard deviation for the sensor calibration of those tips exceeds the expected amount. In those cases, PC-DMIS displays a message to ask if you want to repeat the calibration of those tips. If you click Yes, the system uses the offsets and orientation determined by the first measurement rather than the theoretical values. This results in a clipping around the target that is more accurate during this re-calibration.
You can calibrate the CWS tip offset on a sphere. Sphere tools with a less reflective surface work better than those with a highly reflective surface. Calibration is supported on fixed mount multi-sensor machines and on indexing wrists with a TKJ connector.
The calibration executes using the current temperature compensation.
The measurement range of most CWS probe heads is small. This can mean the manual point taken when the tool has moved or when using the Manual+DCC motion must be very close to the sphere pole or nearest point for the calibration to execute successfully.
During calibration execution, the machine automatically moves to the center of the CWS measurement range, or to the needed measurement range position for each point.
PC-DMIS does not support multiple wrist angle tip calibration in a single calibration operation. You must calibrate each tip separately.
When you calibrate a wrist angle tip for the first time and the tool has not moved, select Man+DCC. For all subsequent measurements of this tip, select DCC.
There are no automatic clearance moves before or after the calibration measurement sequence. Ensure clearance for any wrist rotation needed to position the wrist for the specified tip before starting the calibration. Ensure probe clearance for the move to the measurement start position.
The following steps outline the procedure to calibrate your laser sensor for the first time:
Select the Insert | Hardware Definition | Probe menu item.
In the Probe Utilities dialog box, define the CWS probe and tip.
Select Measure to open the Calibrate Probe Offset dialog box.
Configure the settings and select Calibrate.
Indicate if the qualification tool has moved.
If you select Yes, PC-DMIS displays the Execution dialog box and prompts you to take a manual point. The point should be at the top or nearest point of the sphere from the perspective of the probe and probe vector. If you select No, PC-DMIS displays the Execution dialog box and begins DCC measurement.
After the calibration measurement completes, click Results in the Probe Utilities dialog box to see detailed results.

 Mapping
Infinite Wrist DCC CMS Laser Sensors
Mapping
Infinite Wrist DCC CMS Laser Sensors
A hardware configuration of a CMS laser sensor and an infinitely indexable wrist, such as the CW43L, has the ability to qualify infinite tip orientations. You can define the tip orientations by wrist angles A, B, and C through a Laser Wrist Map (LWM). You can create a LWM if you qualify a grid of tip orientations that cover the specified range of angles A, B, and C.
Once you create the LWM for a specific sensor, you can add new tips to the sensor and if those tips are within the angle range that you specified during map creation, they are automatically qualified and you can begin measuring.
You need to recreate the LWM each time a component of the wrist changes (for example, when the CJoint changes). Also, refer to your hardware and vendor information for the appropriate times to map a wrist since this can change based on the device construction and manufacturer recommendations.
The following steps outline the procedure for mapping infinite wrist DCC CMS laser sensors:
Define the sensor:
In the Probe Utilities dialog box, create a sensor as indicated below:
Infinitely indexable wrist, such as the CW43L
CJoint
CMS laser sensor
For example:
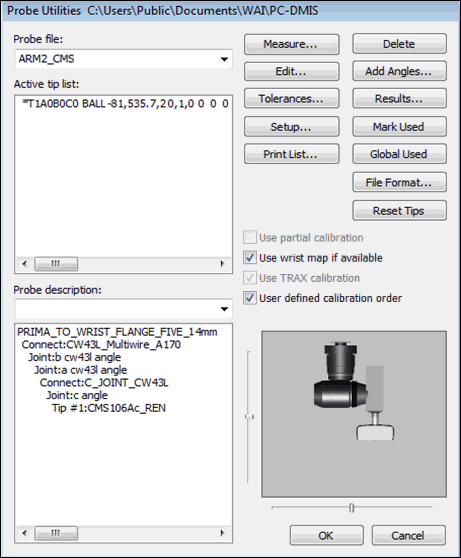
Sample Probe Utilities dialog box with a CMS laser sensor and an indexable wrist
Select the Use wrist map if available check box.
Click Measure to display the Measure Probe dialog box.
For example:
Create the map:
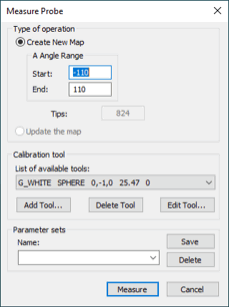
From the Measure Probe dialog box, select the Create New Map option.
For A Angle Range, type the desired Start and End values. These values define a range of angles that form a virtual cone. The map qualifies any tip orientations that fit in this virtual cone.
The B and C angles are always mapped within the full physical range (typically, -180 to +180 degrees).
The Tips box displays the total number of tips measured to create the map.
Click Measure.
PC-DMIS measures five sensor orientations around the sphere tool.
PC-DMIS measures all of the tips in the mapping grid.
Updating an Existing Map
Once you create the map, you can recover the correct qualification for all of the tips whenever a geometrical or thermal parameter of the Sensor - Wrist system changes. For example, after the sensor experiences a physical collision, or when the room temperature changes.
To recover the correct qualification:
From the Measure Probe dialog box, select the Update the map option.
Click Measure. PC-DMIS starts to re-measure the same five sensor orientations around the sphere tool as it measured during the map creation process.
Resuming Map Creation
If the process of creating a map is interrupted (because the machine powered down, you were interrupted, or some math calibration errors occurred, for example), a Resume option appears in the Measure Probe dialog box. You can use this option to continue creating the map.
To resume the process of creating a map:
Select the Resume option in the Measure Probe dialog box. PC-DMIS automatically calculates which tips are still missing in the current map and creates a list of the missing tips to be measured.
You are not able to use the Resume option again until PC-DMIS successfully completes the mapping.
Click Measure. PC-DMIS starts to measure the tips necessary to complete the map.
Defining Parameter Sets for Map Creation
You can define a parameter set to create a map. You can also use the AUTOCALIBRATE command within a measurement routine to update a map.
To define a parameter set:
In the Measure Probe dialog box, select and enter the desired values.
In the Name box, type a name for the parameter set.
Click Save.
To close the dialog box, click Cancel.
For more information about parameter sets and how to use the AUTOCALIBRATE command, see "Dual Arms with Wrists Calibration Example" in the PC-DMIS Core documentation.
More:
Manually Bisecting the Calibration Sphere