REFERENCE Method
The OFFSETFLAT method measures the edge thickness relative to the end point. This method creates a line that is parallel to the end point and is the LE_OFFSET parameter away from the end point. This intersects the line with the mean camber line (MCL) and yields the MCL intersection point.
The OFFSETFLAT method uses the direction of the surface at the end point. Measured splines are sometimes a little wiggly, which can make the end-point direction unrepeatable from blade to blade. To make end-point directions more stable, you can define the parameters for the LE_FLAT_SIZE and TE_FLAT_SIZE keywords in the Tolerance file. The parameters specify the diameter of a circular zone that is centered on the end point. PC-DMIS Blade fits a least-squares line to everything inside the zone and defines the direction of that least-squares line to be the end-point direction used in the OFFSETFLAT method.
After the OFFSETFLAT method identifies the MCL intersection point, the NORMAL, SQUARE, and XWIDTH-YWIDTH calculation methods continue with the measurement as follows:
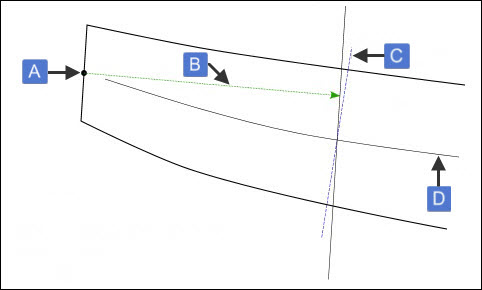
The NORMAL method measures the edge thickness perpendicularly to the MCL and through the MCL intersection point. For example:

Example of NORMAL and OFFSETFLAT methods
A -Edge point
B - LE_OFFSET
C - Edge thickness perpendicular to MCL
D - MCL
The XWIDTH-YWIDTH method reports the X component and Y component, respectively, of the edge thickness perpendicularly to the MCL.
The SQUARE method measures the edge thickness through the MCL intersection point and parallel to the end point. For example:
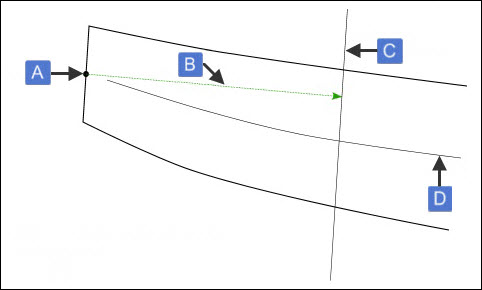
Example of SQUARE and OFFSETFLAT methods
A - Edge point
B - LE_OFFSET
C - Edge thickness parallel to edge point
D - MCL
The OFFSETFLAT method is available for the following calculations:
LETHCK
LETHCK2-10
TETHCK
TETHCK2-10
More:
MCL Calculation Method