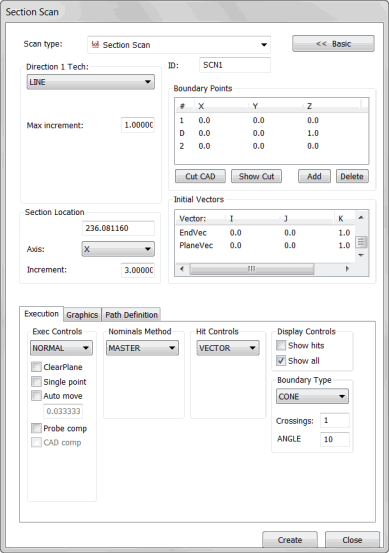

Section Scan dialog box
The Insert | Scan | Section scan is very similar to the Linear Open scan. It scans the surface along a line on the part. This type of scan is available only when CAD surface data is available. With CAD surface data, PC-DMIS will detect a Start Point and End Point at the section. Section scans use the starting and ending point for the line, and also include a direction point. The probe will always remain within the cut plane while doing the scan.
There are three types of section scan direction techniques.
Detect and Skip Holes
Section scans have the ability to detect holes and then skip them while scanning along a part. This type of scan enables you to select "section lines" drawn on the screen by the CAD engineer and then continue the scan.
Multiple Scans Along a Fixed Axis
One advantage to using a section scan is the ability to do multiple scans along a fixed axis.
Suppose you want to scan a line along the Y axis at
a certain increment along the X axis. Therefore:
At X = 5.0, you want to scan your first line.
At X = 5.5, you want to scan your second line.
At X = 6.0, you would scan your third line.
You could do this with several linear open scans, but you can accomplish these types of incremental scans with the section scan.
To do this, you would set up the section scan with the X axis as the section axis and 0.5 as the section increment. You should also set additional parameters (see "Performing a Linear Open Advanced Scan"). After the scan is measured, PC-DMIS will re-display the Section Scan dialog box with all of the boundary points shifted to the next section by the increment you specified.
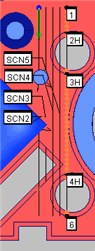
Sample incremental scans
To Create a Section Scan
Ensure that you have a TTP or an analog probe enabled.
Place PC-DMIS into DCC mode.
Select Insert | Scan | Section from the submenu. The Section Scan dialog box appears.
If you want to use a custom name, type the name of the scan in the ID box.
Select the appropriate SECTION type for the first direction from the Direction 1 Tech list. Depending on the technique selected, type the appropriate increment and angle values into the Max Incr, Min Incr, Max Angle, and Min Angle boxes.
If your scan traverses multiple surfaces, consider selecting surfaces by using the Select check box as discussed in the "Graphics Tab" topic.
Add the 1 point (starting point, the D point (direction to scan) and the 2 point (ending point) for the section scan. This will select a line that you wish to scan. Pick these points by following an appropriate procedure as discussed in the "Boundary Points area" topic.
Select the Cut CAD button. This cuts the scan up into subsections, and shows, the locations that PC-DMIS will skip because of obstructions (such as holes) along the surface. You can click the Show Bnd button to show the boundary points again.
In the Section Location area, do the following:
From the Axis list, select the axis along which subsequent section scans will increment.
Type the location value for that axis that you want set for all the boundary points.
Type the increment value in the Increment box. This is the amount that PC-DMIS will shift the scan after you click the Create button.
Select the appropriate type of hits to take from the Hit Type list in the Hit Controls area.
Make any needed changes to the vectors in the Initial Vectors area. To do this, double-click on the vector, make any changes to the Edit Scan Item dialog box, and then click OK to return to the Section Scan dialog box.
Select the appropriate nominals mode from the Nominals list in the Nominals Method area.
In the Tolerance box in the Nominals Method area, type a tolerance value that at least compensates for the probe's radius.
Select the appropriate execution mode from the Execute list in the Exec Control area.
If you are using a thin part, type the part's thickness in the Thickness box on the Graphics tab.
If needed, select any of the check boxes from the areas on the Execution tab.
If using an analog probe, consider using the Control Points tab to run your scan optimally.
Click the Generate button in the Theoretical Path area on the Path Definitions tab to generate a preview of the scan on the CAD model in the Graphic Display window. When you generate the section scan, PC-DMIS will start the scan at the start point and follow the chosen direction, skipping over holes, until it reaches the boundary point.
If needed, you can delete individual points. To do this, select them one at a time from the Theoretical Path area and press the Delete key.
If desired, use the Spline Path area in the same tab to fit the theoretical path to a spline path.
Make additional modifications to your scan as needed.
Click the Create button. PC-DMIS inserts the scan into the Edit window.
After the scan is created, PC-DMIS then shifts the boundary points along the selected axis by the specified increment. It displays the new boundaries it in the Graphic Display window. It lets you use the Section Scan dialog box again to create another section scan.